
Each module within the operating system has been designed for a specific task and is marked accordingly so that it can be accessed automatically when needed. Modules are components with a user interface that are executed in the foreground, visible to the user. An agent is called either by another component or by the system – for example, in response to certain triggers such as push notifications or other on-screen processes. Fuchsia OS focuses on two types of components: modules and agents.Ĭomponents in the role of an agent work in the background and provide services for other components. Components always run in their own sandbox, access objects via namespaces, and publish them via an export directory. The parts of a component include a manifest file as well as the associated code. Each component performs a specific task and can be combined with other components to enable complex applications. The latter are called components in Google terminology.įuchsia components come closest to what we call apps today. A package is a selection of files – including metadata, manifest files, and executable elements.
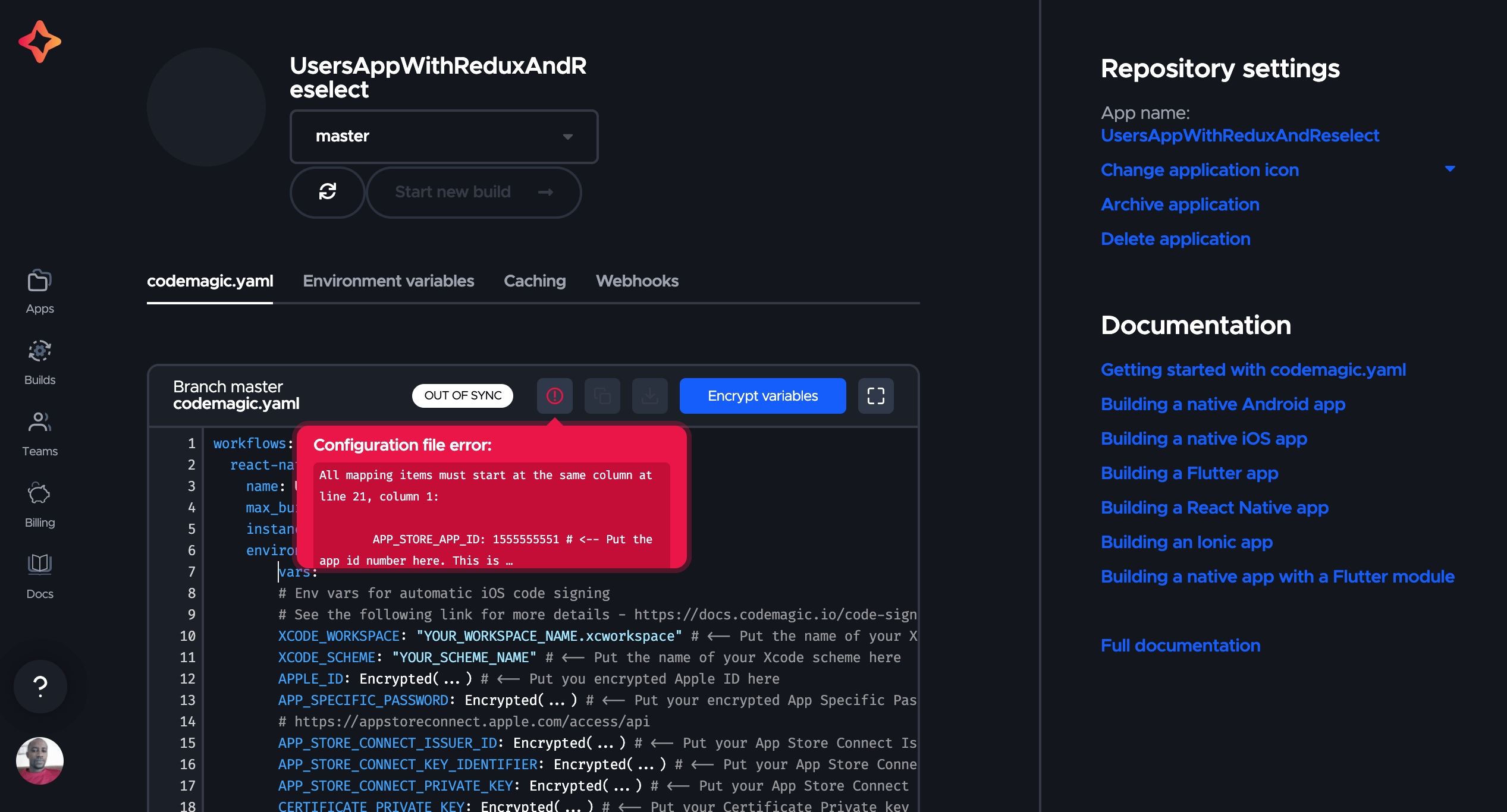
Software units are referred to as packages. Google Fuchsia is based on a modular design that breaks the concept of the app.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
